IN GAME COLLECTABLES
ROLE
Game Engine Integration Engineer
SUMMARY
In Game Collectables partners with game studios to enable players to create physical once-off edition collectables of their customised, in-game avatars. We use cutting edge NVIDIA differentiable rendering tech along with Stratasys additive manufacturing to produce production quality collectables of in-game avatars. We have partnerships with NVIDIA AI, Callaghan Innovation and work with some of New Zealand's best game studios.
I was solely responsible for developing the plugins for both Unreal Engine and Unity. They were used within games to enable us to recreate printable character meshes within the In Game Collectables platform. Some of my tasks included capturing and rendering images during runtime, creating JSON files and dealing with connecting and uploading files to the platform.
I maintained the repositories for the plugins and created user-friendly documents and instructions. I also collaborated with clients and provided support to figure out the ideal method of integration of our plugin into their game environment.
TOOLS
Unreal Engine, Unity, C++, C#, Blender, Github
YEAR
2023 - 2024
COMPANY
In Game Collectables
LINKS
FULLY INTEGRATED GAMES
Pipeline Summary
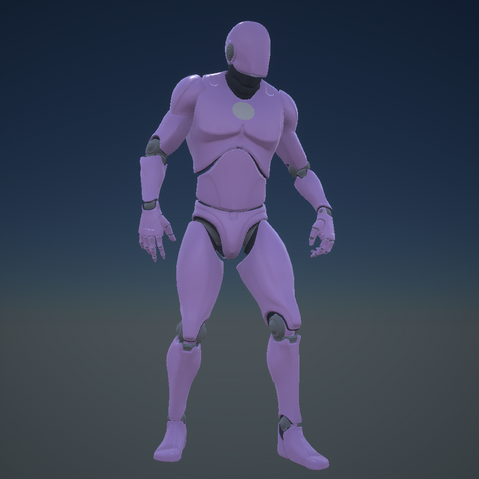
At In Game Collectables, we recreate a character mesh to become a 3D-printable collectable. To achieve this, we need to take multiple captures from different angles and record the camera positions at each angle within a JSON file. These files will then get uploaded to the In Game Collectables platform which will then process the information and recreate the mesh.
After the upload is done, the platform will return an image of a QR code, which will link to a checkout page that the user can purchase their soon-to-be printed character from.
Development
Game Engines
After our research into popular game engine amongst New Zealand game companies, I created lightweight plugins for both Unreal Engine and Unity, as these two engines had the highest demand.
The plugin for Unreal Engine was originally created in UE4.27 and I created a branch within Github for UE5. This way, both could be updated with the least amount of doubling up on work.
Capturing and Rendering
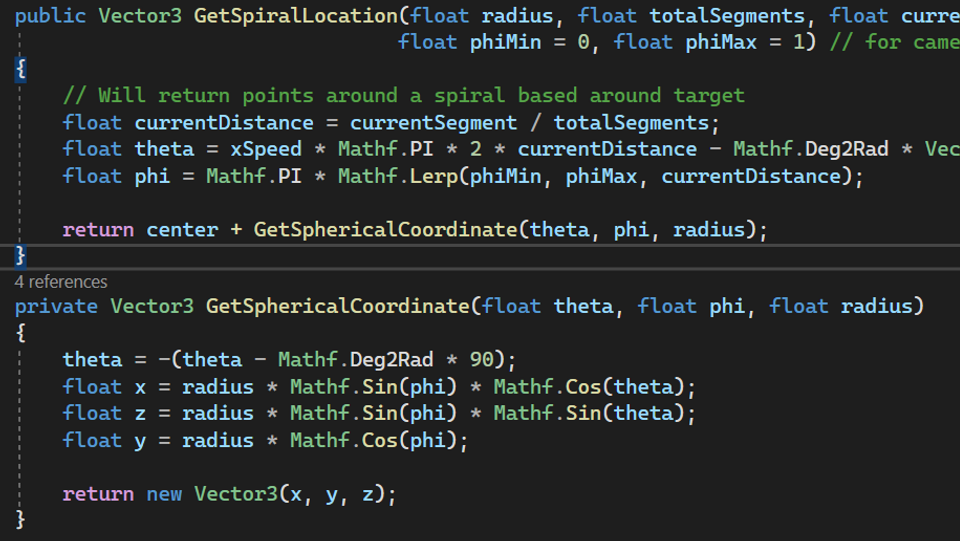
The In Game Collectables platform need image captures and a JSON file of camera information to create a mesh. To get an even capture of the whole mesh, I created an adjustable spiral to control the camera path.
Using the SceneCaptureComponent2D within Unreal Engine, I was able to get renders of characters. One issue was that the colour space and possible rendering methods are already preset within UE, and what we wanted was not available. To get around this, I used two different SceneCaptureComponent2Ds. One camera was used to capture the Final Colour, and one camera was used to capture the mask of the character. By using both of these cameras' render targets as textures within a material, the final masked image could be rendered out.
JSON Creation
After getting the captures, I needed to record the camera transforms and any extra information within an easy to parse file to pass through the rest of the pipeline. I had to record everything within a JSON file, but as I wanted to support both UE4 and UE5, this had to be done in C++ because there is no native blueprint support for JSON file editing in UE4.
The easiest way to deal with JSONs were by creating a custom struct and converting it straight into a JSON format.
Connecting to Platform API
Most of the functionality I needed for this task was only available in C++, so I made a base CaptureUploader C++ class which was then extended to blueprint.
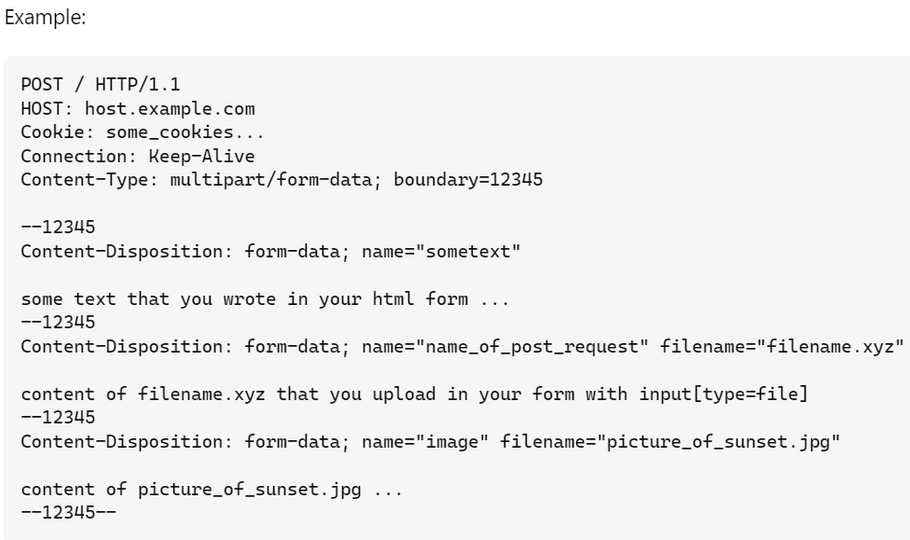
After capturing and exporting all needed files, all the files needed to be sent to the IGC Platform through an API request. As there were many files, they all needed to be sent through as a HTTP multipart/form-data request but Unreal Engine did not have an easy way to handle multipart requests. Instead, the multipart structure had to be recreated with bytes and all files were also encoded into it.
After the files were all uploaded successfully, the API would return a QR code which would lead to the checkout page of the newly created model. The QR code would be generated on the fly within the platform.
This is sent through as a part of the response and the QR code image would need to be decoded from bytes. The new image is then sent through one of the events the plugin user has access to.
Documentation and Maintenance
Github Documentation
To make it accessible as possible for the largest amount of people, both the Unreal Engine and Unity plugins are publicly available on Github with documentation. The documentation comes with instructions, warnings and examples to get the best quality output possible.
Github Maintenance
Though the Unity plugin is pretty compatible across engine versions, new versions of Unreal Engine aren't as easy to work with. To lessen the amount of work I would have to redo for newer engine versions and cut down on doubling up work when the plugin would need to be updated, I made the most of branching within Github to support a UE5 plugin based on the UE4 version.